Fitting the outcome model
Malcolm Barrett
Stanford University
Outcome Model
✅ This will get us the point estimate
❌ This will get NOT us the correct confidence intervals
📦 Let’s bootstrap them with rsample
1. Create a function to run your analysis once on a sample of your data
fit_ipw <- function(.split, ...) {
.df <- as.data.frame(.split)
# fit propensity score model
propensity_model <- glm(
qsmk ~ sex +
race + age + I(age^2) + education +
smokeintensity + I(smokeintensity^2) +
smokeyrs + I(smokeyrs^2) + exercise + active +
wt71 + I(wt71^2),
family = binomial(),
data = .df
)
# calculate inverse probability weights
.df <- propensity_model |>
augment(type.predict = "response", data = .df) |>
mutate(wts = wt_ate(.fitted, qsmk, exposure_type = "binary"))
# fit correctly bootstrapped ipw model
lm(wt82_71 ~ qsmk, data = .df, weights = wts) |>
tidy()
}2. Use {rsample} to bootstrap our causal effect
2. Use {rsample} to bootstrap our causal effect
# Bootstrap sampling with apparent sample
# A tibble: 1,001 × 2
splits id
<list> <chr>
1 <split [1566/592]> Bootstrap0001
2 <split [1566/571]> Bootstrap0002
3 <split [1566/583]> Bootstrap0003
4 <split [1566/579]> Bootstrap0004
5 <split [1566/592]> Bootstrap0005
6 <split [1566/577]> Bootstrap0006
7 <split [1566/578]> Bootstrap0007
8 <split [1566/579]> Bootstrap0008
9 <split [1566/578]> Bootstrap0009
10 <split [1566/581]> Bootstrap0010
# ℹ 991 more rows2. Use {rsample} to bootstrap our causal effect
2. Use {rsample} to bootstrap our causal effect
2. Use {rsample} to bootstrap our causal effect
# Bootstrap sampling with apparent sample
# A tibble: 1,001 × 3
splits id boot_fits
<list> <chr> <list>
1 <split [1566/592]> Bootstrap0001 <tibble [2 × 5]>
2 <split [1566/571]> Bootstrap0002 <tibble [2 × 5]>
3 <split [1566/583]> Bootstrap0003 <tibble [2 × 5]>
4 <split [1566/579]> Bootstrap0004 <tibble [2 × 5]>
5 <split [1566/592]> Bootstrap0005 <tibble [2 × 5]>
6 <split [1566/577]> Bootstrap0006 <tibble [2 × 5]>
7 <split [1566/578]> Bootstrap0007 <tibble [2 × 5]>
8 <split [1566/579]> Bootstrap0008 <tibble [2 × 5]>
9 <split [1566/578]> Bootstrap0009 <tibble [2 × 5]>
10 <split [1566/581]> Bootstrap0010 <tibble [2 × 5]>
# ℹ 991 more rows2. Use {rsample} to bootstrap our causal effect
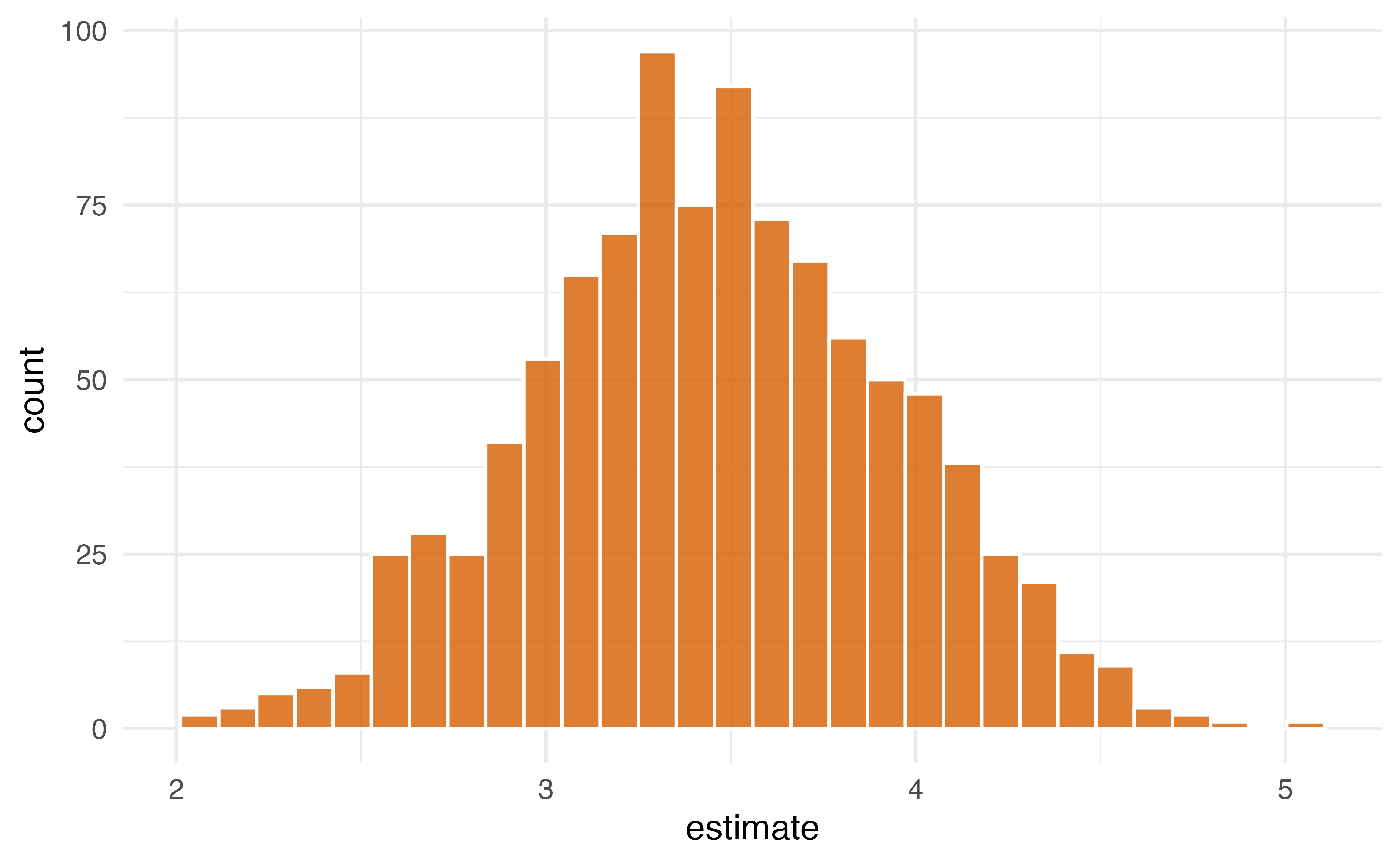
3. Pull out the causal effect
# A tibble: 1 × 6
term .lower .estimate .upper .alpha .method
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 qsmk 2.49 3.46 4.38 0.05 student-tYour Turn
08:00